Guide in SHENZHEN
In the depth of entrepreneurship
/ Live at Shenzhen / Startup at Shenzhen /


Guide in SHENZHEN
In the depth of entrepreneurship
/ Live at Shenzhen / Startup at Shenzhen /

In the depth of entrepreneurship
/ Live at Shenzhen / Startup at Shenzhen /
Choosing the Right Company Type

Foreword
ReadingGuide

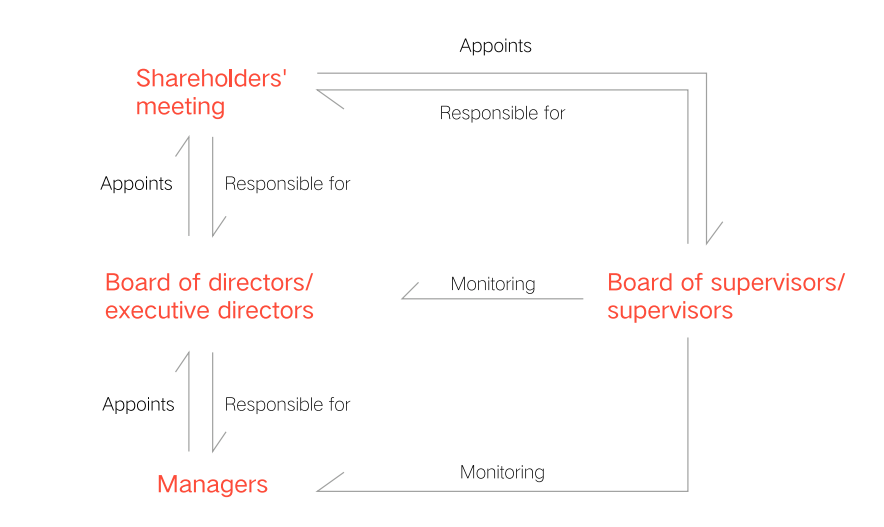
Enterprise types
| Enterprise types | Definitions |
| Foreign-invested Limited Liability Company | A foreign-invested limited liability company refers to an enterprise wholly or partly invested by foreign investors and registered and established in China in accordance with Chinese laws. It includes sole proprietorship of natural person, sole proprietorship of enterprise legal person or foreign investment (non sole proprietorship). |
| Foreign-invested Partnership Enterprise | A partnership enterprise fefers to an enterprise established in China by two or more foreign enterprises or individuals, and a partnership enterprise established in China by a foreign enterprise or individual and a Chinese natural person, legal person or other organization. A foreign-invested partnership is composed of general partners and limited partners. |
| Representative Office | An administrative organization established in China that engages in non-profit activities related to the operations of the foreign company, and is the representative for the foreign company in activities such as communication, product marketing, market surveys, and technology exchange. |
| Foreign-invested Joint Stock Company | Foreign-invested founded joint stock company refers to an enterprise legal person whose total capital is composed of equal shares, the shareholders are responsible for the company with the shares they have subscribed for, the company is liable for the company's debts with all its properties, the shares of the company jointly held by Chinese and foreign shareholders, and the shares purchased and held by foreign shareholders account for more than 25% of the company's registered capital. [This type is rare and will not be described in details in this book] |
| 企业类型 | Pros | Cons |
| Foreign -invested Limited Liability Company | (1) The shareholders can own 100% equity and operate independently without having to consider the position of Chinese investors. The company can determine its own strategic goals and set up a company through joint venture; (2) Compared to the restricted operations of the representative office, a foreign-invested limited liability company can receive revenues in RMB and issue invoices; (3) No minimum registered capital requirements - shareholders may decide on an appropriate amount of registered capital according to the company’s future development needs. If the capital becomes insufficient later on for the company’s operation, it can be increased; (4) No currency restrictions for registered capital - in addition to the commonly used RMB, other foreign currencies (such as Hong Kong dollars / US dollars, etc.) may be used as for registered capital. |
(1) Allowed to be set up only as one single-member limited liability company. (2) A foreign-invested limited liability company must not only have a foreign shareholder, but it is also required to register its general manager, supervisor, finance manager and other personnel roles with the business registration authorities. |
| Foreign -invested Partnership Enterprise | (1) No need to be approved by the competent commercial department; (2) To appoint an executive partner (appointed representative) to carry out partnership affairs, the management organization is simple and flexible, and the decision-making efficiency is high; (3) No need to pay corporate income tax, avoiding double taxation, and effectively reducing the operating costs of enterprises. |
(1) In the catalogue of encouraged and restricted foreign-invested industries in the Catalogue for the Guidance of Industries for Foreign Investment, there are a number of industries that require no foreign investment partnerships be established; (2) The general partner shall bear unlimited joint and several liability for the debt of the partnership, and the limited partner shall be liable for the partnership debt to the limit of the amount of capital contribution he has subscribed, but the limited partner is prohibited by law from exercising the management right of the partnership |
| Representative office | (1) The capital contribution required is lower; (2) Allowed to conduct market surveys, project enquiries and other tasks for the foreign parent company. |
(1) Restricted in terms of commercial operations - a representative office is not allowed to conduct business, issue invoices, etc.; (2) Despite receiving no direct trade and sales income, it is required to pay corporate income tax, employees’ personal income tax, etc. |
Case Study
| Enterprise types | Definitions |
| Foreign-invested Limited Liability Company | (1) A rented office in Shenzhen; (2) Sufficient start-up capital; (3) One legal representative (If the shareholder is a foreign natural person, he / she may act as the shareholder himself / herself, or concurrently serve as the executive director and general manager); (4) One supervisor (who cannot be a director or manager); (5) A finance manager and tax executive;(6) Recipient of legal documents (a Chinese natural person or Chinese enterprise). |
| Foreign-invested Partnership Enterprise | (1) A rented office in Shenzhen; (2) Sufficient start-up capital; (3) At least 2 partners(enterprise or individual); (4) If the executive partner is a company, an appointed representative shall also be established; (5) A credit certificate issued by the general partner;(6) A finance manager and tax executive;(7) Recipient of legal documents (a Chinese natural person or Chinese enterprise). |
| Representative Office | (1) One appointed chief representative (main officer in charge of the company);The company may appoint one to three representatives as required, but not more than four; (2) For companies that have been established for more than two years and have an office and residence overseas, the details of such office and residence may be shown as supporting evidence; (3) A bank account is required for the foreign company, where the bank’s proof of the company’s funds and credit may be shown as supporting evidence. |



enterprise_1622366673027.png)

Choosing the Right Company Type

Foreword
ReadingGuide


Enterprise types
| Enterprise types | Definitions |
| Foreign-invested Limited Liability Company | A foreign-invested limited liability company refers to an enterprise wholly or partly invested by foreign investors and registered and established in China in accordance with Chinese laws. It includes sole proprietorship of natural person, sole proprietorship of enterprise legal person or foreign investment (non sole proprietorship). |
| Foreign-invested Partnership Enterprise | A partnership enterprise fefers to an enterprise established in China by two or more foreign enterprises or individuals, and a partnership enterprise established in China by a foreign enterprise or individual and a Chinese natural person, legal person or other organization. A foreign-invested partnership is composed of general partners and limited partners. |
| Representative Office | An administrative organization established in China that engages in non-profit activities related to the operations of the foreign company, and is the representative for the foreign company in activities such as communication, product marketing, market surveys, and technology exchange. |
| Foreign-invested Joint Stock Company | Foreign-invested founded joint stock company refers to an enterprise legal person whose total capital is composed of equal shares, the shareholders are responsible for the company with the shares they have subscribed for, the company is liable for the company's debts with all its properties, the shares of the company jointly held by Chinese and foreign shareholders, and the shares purchased and held by foreign shareholders account for more than 25% of the company's registered capital. [This type is rare and will not be described in details in this book] |
| 企业类型 | Pros | Cons |
| Foreign -invested Limited Liability Company | (1) The shareholders can own 100% equity and operate independently without having to consider the position of Chinese investors. The company can determine its own strategic goals and set up a company through joint venture; (2) Compared to the restricted operations of the representative office, a foreign-invested limited liability company can receive revenues in RMB and issue invoices; (3) No minimum registered capital requirements - shareholders may decide on an appropriate amount of registered capital according to the company’s future development needs. If the capital becomes insufficient later on for the company’s operation, it can be increased; (4) No currency restrictions for registered capital - in addition to the commonly used RMB, other foreign currencies (such as Hong Kong dollars / US dollars, etc.) may be used as for registered capital. |
(1) Allowed to be set up only as one single-member limited liability company. (2) A foreign-invested limited liability company must not only have a foreign shareholder, but it is also required to register its general manager, supervisor, finance manager and other personnel roles with the business registration authorities. |
| Foreign -invested Partnership Enterprise | (1) No need to be approved by the competent commercial department; (2) To appoint an executive partner (appointed representative) to carry out partnership affairs, the management organization is simple and flexible, and the decision-making efficiency is high; (3) No need to pay corporate income tax, avoiding double taxation, and effectively reducing the operating costs of enterprises. |
(1) In the catalogue of encouraged and restricted foreign-invested industries in the Catalogue for the Guidance of Industries for Foreign Investment, there are a number of industries that require no foreign investment partnerships be established; (2) The general partner shall bear unlimited joint and several liability for the debt of the partnership, and the limited partner shall be liable for the partnership debt to the limit of the amount of capital contribution he has subscribed, but the limited partner is prohibited by law from exercising the management right of the partnership |
| Representative office | (1) The capital contribution required is lower; (2) Allowed to conduct market surveys, project enquiries and other tasks for the foreign parent company. |
(1) Restricted in terms of commercial operations - a representative office is not allowed to conduct business, issue invoices, etc.; (2) Despite receiving no direct trade and sales income, it is required to pay corporate income tax, employees’ personal income tax, etc. |
Case Study
| Enterprise types | Definitions |
| Foreign-invested Limited Liability Company | (1) A rented office in Shenzhen; (2) Sufficient start-up capital; (3) One legal representative (If the shareholder is a foreign natural person, he / she may act as the shareholder himself / herself, or concurrently serve as the executive director and general manager); (4) One supervisor (who cannot be a director or manager); (5) A finance manager and tax executive;(6) Recipient of legal documents (a Chinese natural person or Chinese enterprise). |
| Foreign-invested Partnership Enterprise | (1) A rented office in Shenzhen; (2) Sufficient start-up capital; (3) At least 2 partners(enterprise or individual); (4) If the executive partner is a company, an appointed representative shall also be established; (5) A credit certificate issued by the general partner;(6) A finance manager and tax executive;(7) Recipient of legal documents (a Chinese natural person or Chinese enterprise). |
| Representative Office | (1) One appointed chief representative (main officer in charge of the company);The company may appoint one to three representatives as required, but not more than four; (2) For companies that have been established for more than two years and have an office and residence overseas, the details of such office and residence may be shown as supporting evidence; (3) A bank account is required for the foreign company, where the bank’s proof of the company’s funds and credit may be shown as supporting evidence. |



enterprise_1622366673027.png)
